Alternative treatments for diabetes are rising in popularity as more and more people seek options outside of traditional insulin therapy. For those living with diabetes, it’s important to know that insulin isn’t the only game in town. This blog post will explore these alternative treatments, shedding light on their benefits, risks, and how they stack up against insulin. From diet and exercise modifications to experimental therapies, we’ll dive deep into the world of diabetic care. So if you’re looking to broaden your understanding of diabetes management, you’re in the right place. Let’s get started!
Understanding Diabetes and Insulin
Diabetes is a complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic disease characterized by high blood sugar levels, either due to the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or its inability to effectively use the insulin it produces. In this section, we will delve into the basics of diabetes and how insulin works to manage this condition.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition that disrupts the way our bodies process glucose, which is the primary source of energy for our cells. When we consume food, our bodies break down carbohydrates into glucose, which then enters our bloodstream. Normally, the pancreas releases a hormone called insulin, which helps regulate glucose levels in the blood.
In individuals with diabetes, this process is impaired. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body produces little to no insulin.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is more common and occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to meet the body’s needs. This type of diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary behavior, and poor diet.
How Does Insulin Work?
Insulin plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. It acts as a key that unlocks the cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy. When glucose levels in the blood rise after a meal, the pancreas releases insulin to signal cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream.
Once inside the cells, glucose can be used immediately for energy or stored for later use. Insulin also helps facilitate the storage of excess glucose in the liver and muscles as glycogen. This stored glycogen can be converted back into glucose when the body needs an additional energy boost.
In individuals with diabetes, the lack of insulin or the body’s inability to effectively use it leads to elevated blood glucose levels. This can have detrimental effects on various organs and tissues in the body, including the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
Managing diabetes often involves the use of insulin therapy, which aims to regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin can be administered through injections, insulin pumps, or inhalation devices, depending on the individual’s needs and preferences.
 Diabetic Person Using A Pen Insulin Self Injection (Photo by Artem Podrez)
Diabetic Person Using A Pen Insulin Self Injection (Photo by Artem Podrez)
Understanding how diabetes and insulin work together is crucial for individuals living with this condition. By gaining knowledge about the mechanisms behind diabetes and insulin, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options and better manage their blood sugar levels.
In the next sections, we will explore alternative treatments for diabetes beyond insulin, offering insights into how individuals can take control of their health and improve their quality of life.
Beyond Insulin: Exploring Alternative Treatments for Diabetes
The Limitations of Insulin Therapy
Living with diabetes can be a daily challenge, and for many individuals, insulin therapy becomes a necessary part of their treatment plan. While insulin is a crucial medication that helps manage blood sugar levels, it is important to understand its limitations. In this section, we will delve into the side effects of insulin and the challenges associated with its administration.
Side Effects of Insulin
Insulin therapy comes with its fair share of side effects that can impact the well-being and quality of life of individuals with diabetes. It is crucial to be aware of these potential side effects and manage them effectively. Here are a few commonly experienced side effects:
- Hypoglycemia: Insulin can sometimes cause blood sugar levels to drop too low, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, trembling, sweating, and confusion. This can be especially dangerous if not addressed promptly.
- Weight Gain: Insulin may cause weight gain in some individuals due to its role in promoting the storage of fat. This can be frustrating for those trying to manage their weight or achieve weight loss goals.
- Injection Site Reactions: Some individuals may experience redness, itching, or swelling at the site of insulin injections. These reactions can be bothersome and may require special care to prevent infection.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, allergic reactions to insulin can occur. Symptoms may include rash, itching, shortness of breath, or swelling. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if any signs of an allergic reaction are noticed.
Challenges in Insulin Administration
Administering insulin can be a complex process that presents its own set of challenges. From finding the right dosage to dealing with the logistics of injections, these challenges can be overwhelming for individuals with diabetes. Here are a few common challenges faced in insulin administration:
- Injection Technique: Proper injection technique is crucial for effective insulin delivery. It can be difficult to master the skill of injecting insulin, especially for those who are newly diagnosed or have limited dexterity. Ensuring consistent and accurate injections is essential for optimal diabetes management.
- Consistency in Dosage: Determining the right dosage of insulin can be a trial-and-error process. Factors such as food intake, physical activity, stress levels, and illness can all affect insulin requirements. Achieving consistency in dosage can be challenging, and adjustments may need to be made frequently to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Travel and Storage: For individuals who travel frequently or have a busy lifestyle, carrying and storing insulin can be a logistical challenge. Ensuring that insulin is stored at the proper temperature and maintaining a sufficient supply while on the go requires careful planning and preparation.
- Needle Phobia: Fear of needles can be a significant barrier to insulin therapy for some individuals. Overcoming this fear and developing strategies to manage needle anxiety is crucial for successful insulin administration.
 Equipment in Preventing Diabetes on a Blue Surface (Photo by Nataliya Vaitkevich)
Equipment in Preventing Diabetes on a Blue Surface (Photo by Nataliya Vaitkevich)
In conclusion, while insulin therapy is an essential component of diabetes management, it is important to recognize its limitations. Understanding the potential side effects and challenges associated with insulin administration can help individuals with diabetes explore alternative treatments and improve their overall quality of life. In the next sections, we will explore some of these alternative treatments that go beyond insulin, offering hope for a brighter future in diabetes care.
Exploring Alternative Treatments for Diabetes
Lifestyle Changes and Diet
 Slice of Eggs on Cakes (Photo by Jane Doan)
Slice of Eggs on Cakes (Photo by Jane Doan)
When it comes to managing diabetes, lifestyle changes and a healthy diet play a crucial role in keeping blood sugar levels in check. Making small but impactful modifications to our daily routine can bring about significant improvements in our overall health.
One of the first steps toward managing diabetes is adopting a balanced and nutritious diet. This means incorporating foods that are low in sugar and carbohydrates, while also emphasizing the consumption of lean proteins, whole grains, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. By doing so, we can maintain a steady blood sugar level and promote weight management, which is vital for diabetes control.
In addition to a healthy diet, physical activity is essential for managing diabetes. Regular exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss. Engaging in activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or even dancing can have a positive impact on our overall well-being. It is recommended to aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Oral Medications
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to manage diabetes effectively. This is where oral medications come into play. These medications are designed to lower blood sugar levels by either increasing insulin production, improving insulin sensitivity, or reducing glucose production in the liver.
There are various types of oral medications available, and the choice of medication depends on the individual’s specific needs and medical history. Some commonly prescribed oral medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, and thiazolidinediones. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable oral medication and dosage for each individual.
Injectable Medications
For individuals with more advanced cases of diabetes, injectable medications may be necessary. Injectable medications include non-insulin injectables and insulin. Non-insulin injectables, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, work by either increasing insulin production, reducing glucose production, or improving insulin sensitivity.
Insulin, on the other hand, is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. For individuals with type 1 diabetes, insulin is a vital component of their treatment plan. It may also be prescribed for individuals with type 2 diabetes who cannot effectively manage their blood sugar levels with oral medications alone.
Injectable medications are typically administered using a syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump. The dosage and administration method will depend on the individual’s specific needs and the healthcare provider’s recommendations.
In conclusion, exploring alternative treatments for diabetes goes beyond insulin. Lifestyle changes and a healthy diet form the foundation of diabetes management. Oral medications can provide additional support, while injectable medications may be necessary for more advanced cases. By working closely with healthcare professionals and making the necessary adjustments to our lifestyle and treatment plan, we can effectively manage diabetes and improve our overall well-being.
Beyond Insulin: Exploring Alternative Treatments for Diabetes
Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) Approaches
 Person Putting Needles on the Forehead of a Man (Photo by Antoni Shkraba)
Person Putting Needles on the Forehead of a Man (Photo by Antoni Shkraba)
When it comes to managing diabetes, the focus is often on insulin and medication. However, there are complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) approaches that can be explored alongside traditional treatments. These approaches aim to support overall health and well-being and may provide additional benefits for individuals with diabetes. In this section, we will delve into three popular CAM approaches: acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mind-body therapies.
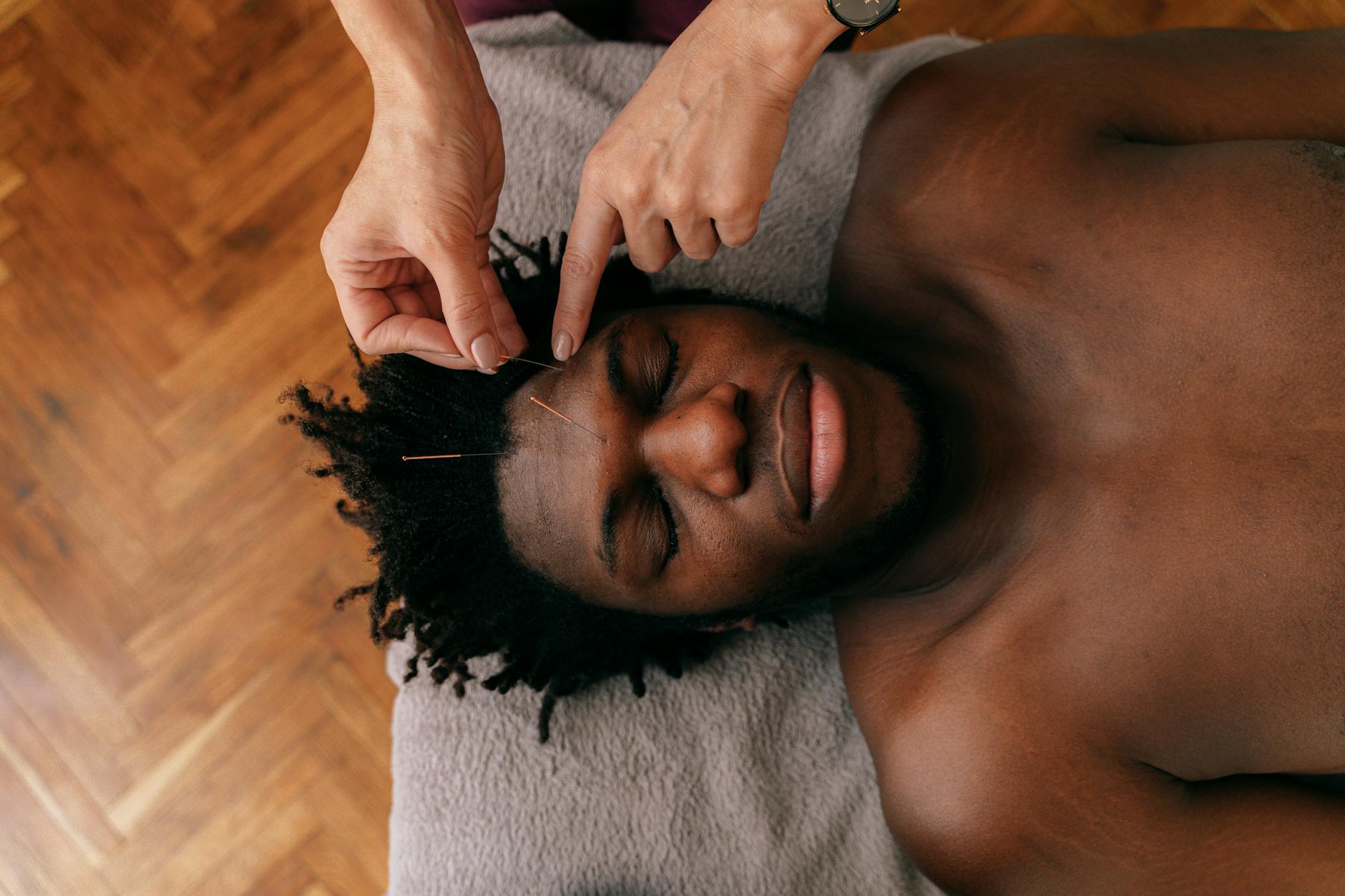
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese practice that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. These acupuncture points are believed to be connected to energy pathways, or meridians, that flow throughout the body. By stimulating these points, acupuncture aims to restore balance and promote healing.
For individuals with diabetes, acupuncture may offer several potential benefits. Studies have suggested that acupuncture may help improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels, and reduce inflammation. Additionally, acupuncture sessions can help alleviate stress, which is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as stress can negatively impact blood sugar control.
Herbal Supplements
 Medication Pill on Green Background (Photo by Nataliya Vaitkevich)
Medication Pill on Green Background (Photo by Nataliya Vaitkevich)
Herbal supplements have long been used in various traditional healing systems to support overall health. In the context of diabetes, certain herbs and botanicals have gained attention for their potential benefits. It’s important to note that while herbal supplements may offer some advantages, they should not replace prescribed medications or insulin therapy.
Some herbal supplements that have shown promise in managing diabetes include:
- Cinnamon: This common spice has been studied for its potential to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
- Gymnema Sylvestre: Traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine, this herb may help reduce cravings for sweets and support healthy blood sugar levels.
- Bitter Melon: Consumed as a vegetable in many Asian cuisines, bitter melon has been found to have blood sugar-lowering properties.
Before incorporating any herbal supplements into your routine, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional, as they can provide guidance on appropriate dosages and potential interactions with other medications.
Mind-Body Therapies
 Woman in Black Leggings Unrolling A Yoga Mat (Photo by Mikhail Nilov)
Woman in Black Leggings Unrolling A Yoga Mat (Photo by Mikhail Nilov)
Mind-body therapies encompass a range of practices that emphasize the connection between the mind, body, and spirit. These therapies can help individuals with diabetes manage stress, improve overall well-being, and promote self-care. Some popular mind-body therapies include:
- Meditation: This practice involves focusing your attention and eliminating the stream of thoughts that may be causing stress. Regular meditation can help reduce stress hormones, lower blood pressure, and improve blood sugar control.
- Yoga: Combining physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation, yoga is a holistic practice that can enhance flexibility, reduce stress, and improve overall fitness. Certain yoga poses may specifically target organs and glands that play a role in blood sugar regulation.
- Tai Chi: A gentle martial art originating from China, Tai Chi involves slow and flowing movements along with deep breathing. Regular practice of Tai Chi has been shown to improve balance, reduce stress, and enhance overall physical and mental well-being.
Incorporating mind-body therapies into your diabetes management plan can provide numerous benefits. These practices not only help reduce stress but also promote mindfulness, which can positively impact blood sugar control.
Remember, while CAM approaches like acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mind-body therapies can offer potential benefits, they should be used as complementary to traditional medical treatments. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment or making changes to your diabetes management plan.
Stay tuned for the next section where we will explore another alternative treatment option for diabetes.
Emerging Technologies and Therapies
The treatment landscape for diabetes is constantly evolving, with researchers and scientists exploring innovative approaches beyond insulin. In this section, we will delve into some of the exciting emerging technologies and therapies that hold promise for the future of diabetes management.
Artificial Pancreas Systems
 Oriental teapot and ceramic cups with ornament on table near burning candles against decorative cushion in living room (Photo by Max Rahubovskiy)
Oriental teapot and ceramic cups with ornament on table near burning candles against decorative cushion in living room (Photo by Max Rahubovskiy)
Artificial Pancreas Systems (APS) have emerged as a groundbreaking technology in diabetes management. These systems aim to mimic the functions of a healthy pancreas by combining continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) with automated insulin delivery. The CGM constantly measures blood glucose levels, while the insulin pump delivers precise doses of insulin based on the readings. This closed-loop system offers a more streamlined and efficient way to keep blood sugar levels stable throughout the day and night.
The APS technology has the potential to revolutionize diabetes care by reducing the burden of frequent glucose monitoring and manual insulin adjustments. It can provide better glycemic control, reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, and improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Gene Therapy
 Person Holding Black Pen on White Paper (Photo by cottonbro studio)
Person Holding Black Pen on White Paper (Photo by cottonbro studio)
Gene therapy presents an exciting avenue for the treatment of diabetes. It involves the introduction of specific genes into the cells of the body to enhance their function or compensate for genetic defects. In the case of diabetes, gene therapy aims to restore normal insulin production.
Researchers are exploring different approaches to gene therapy, including using viral vectors to deliver therapeutic genes into the body. By targeting the cells responsible for insulin production, gene therapy holds the potential to stimulate the production of insulin and regulate blood sugar levels more effectively.
While gene therapy for diabetes is still in the experimental stages, it offers a glimpse into the future of personalized medicine, where treatments can be tailored to an individual’s unique genetic makeup.
Stem Cell Research
 White and Purple Petal Flower Focus Photography (Photo by Anthony 📷📹🙂)
White and Purple Petal Flower Focus Photography (Photo by Anthony 📷📹🙂)
Stem cell research has garnered significant attention in the field of diabetes treatment. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the potential to develop into various specialized cells, including pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin.
Scientists are exploring different sources of stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells, to generate functional pancreatic beta cells. The goal is to replace the faulty or destroyed beta cells in individuals with diabetes, restoring their ability to produce insulin naturally.
While stem cell therapy for diabetes is still in its early stages and faces various challenges, including immune rejection and safety concerns, it holds immense promise as a potential cure for the disease.
In conclusion, emerging technologies and therapies like Artificial Pancreas Systems, gene therapy, and stem cell research offer hope for a future where diabetes management goes beyond insulin injections. These innovative approaches have the potential to revolutionize the way we treat and manage diabetes, ultimately improving the lives of millions of people living with the condition. Stay tuned for more exciting developments in the field of diabetes treatment!
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring alternative treatments for diabetes goes beyond relying solely on insulin. While insulin remains a crucial and lifesaving treatment option for many individuals, it is essential to consider additional approaches that can complement and enhance overall diabetes management. From natural remedies to dietary changes and lifestyle modifications, there are various options available that can help individuals with diabetes achieve better control over their condition and improve their quality of life.
One alternative treatment worth considering is herbal medicine. Numerous herbs, such as cinnamon, bitter melon, and fenugreek, have shown promising effects in improving blood sugar control. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating herbal remedies into your diabetes management plan, as they can interact with other medications or have varying effects on individuals.
Additionally, adopting a healthy and balanced diet plays a significant role in managing diabetes. Foods rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote overall well-being. It is advisable to work with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to create a personalized meal plan that suits your specific needs and preferences.
Moreover, regular physical activity is key to managing diabetes effectively. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercises, such as brisk walking or cycling, can improve insulin sensitivity and promote weight loss, which is beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise routine to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your condition.
Lastly, stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga, can contribute to diabetes management. Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels and overall health, so finding healthy ways to cope with stress is important.
In conclusion, while insulin remains a cornerstone of diabetes treatment, exploring alternative approaches can offer additional benefits and support overall diabetes management. By incorporating herbal remedies, adopting a healthy diet, staying physically active, and managing stress effectively, individuals with diabetes can strive for better control and a higher quality of life. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your treatment plan.